Seamless Production Migration: Moving to Cloudflare Load Balancer
Overview
This article documents our seamless production migration from ANS Load Balancer to Cloudflare Load Balancer for our production care management web application.
Current Setup
Our domain eplancare.com is hosted on Cloudflare as our DNS provider. The production application is accessible at login.eplancare.com, which is our main customer-facing application serving healthcare providers and care managers who access our platform daily.
Currently, login.eplancare.com points to a Virtual IP (VIP) address managed by ANS, a third-party cloud provider in the UK. This VIP routes traffic to the ANS Load Balancer, which then distributes requests across our backend Tomcat web servers.
Migration Goal
We needed to migrate from the ANS Load Balancer to Cloudflare Load Balancer while maintaining the same application endpoint (login.eplancare.com). This migration was driven by operational overhead, security concerns, and the need for automated certificate management. The cutover was executed successfully with zero downtime during a planned maintenance window (10th November 2024, 04:30-05:15 UK Time).
Why We Migrated
Operational Challenges with ANS Load Balancer
Manual Certificate Management
- SSL/TLS certificates required manual upload through the ANS Portal.
- Manual process to delete expiring certificates and upload new ones.
- Limited API functionality for automation.
- High risk of outages due to forgotten certificate renewals.
Security Concerns
- ANS was running HAProxy version 2.0.31, which reached end-of-life on 05th April 2024.
- This version was no longer supported by the HAProxy vendor at the time of migration (October 2025).
- Reference: HAProxy End of Life tracking.
Past Incidents
- We experienced an outage when an SSL/TLS certificate wasn't uploaded in time due to the manual process.
Benefits of Cloudflare Load Balancer
- Automated Certificate Management - Cloudflare handles certificate renewal automatically.
- Global Edge Network - Improved performance and reduced latency.
- Reduced Operational Overhead - No manual certificate uploads.
- Modern Infrastructure - Up-to-date, vendor-supported platform.
Risk Consideration
⚠️ Potential Cloudflare Outage - If Cloudflare experiences issues, we could face downtime
- Mitigation: We kept ANS LB as a backup solution (requires manual switchover, though).
Architecture Overview
The following diagram illustrates the final Cloudflare Load Balancer architecture after migration:

Migration Approach
Phase 1: Proof of Concept
Objective: Validate Cloudflare LB functionality in a lower environment (non-production).
Steps:
- Set up test Cloudflare Load Balancer in lower environment.
- Configured traffic distribution across 2 test web servers.
- Performed comprehensive testing.
Result: Successfully validated.
Phase 2: Planning and Preparation
Implementation Planning
- Developed detailed implementation procedures.
- Created comprehensive rollback plan.
- Practiced both plans in lower environment.
- Special focus on rollback procedures.
Change Control Process
- Documented implementation and rollback plans.
- Coordinated migration date/time with development and operations teams.
- Scheduled during maintenance hours (outside business hours).
- Communicated plans to wider stakeholder audience.
Phase 3: Pre-Configuration
Strategy: Configure everything in advance using a dummy hostname, then switch to production hostname at go-live.
We used a dummy hostname (test.eplancare.com) to set up the entire configuration before switching to the actual production FQDN (login.eplancare.com). This minimised the cutover window.
Cloudflare Load Balancer Configuration
Endpoint Configuration
- Provide
Pool NameandDescription. - Provide
Endpoint NamesandEndpoint IP addresses,PortsandWeightsfor each endpoint. - Steering Method:
Least Outstanding Requests.
Session Affinity Settings
- Method:
Cloudflare cookie only. - Session TTL:
43,200seconds (12 hours). - Endpoint Drain Duration:
60seconds. - Zero Downtime Failover:
Sticky.
Health Check Configuration
- Type:
HTTPS. - Method:
GET. - Port:
8443. - Path:
/healthcheck - Interval:
120seconds (between each health check). - Timeout:
10seconds (before marking as failed). - Retries:
2attempts. - Check Regions:
Western Europe.
Monitor Configuration
- Type:
HTTPS. - Path:
/healthcheck. - Port:
8443.
Note: Health check and monitor configurations were applied to all 4 Tomcat instances (tomcat-01, tomcat-02, tomcat-03, tomcat-04).
Migration Execution
Go-Live: Mon 10th Nov 2025, 04:30 UK Time
Maintenance Page Display
Before draining traffic, I configured custom 503 error pages on all Tomcat web servers (tomcat-01, tomcat-02, tomcat-03, tomcat-04) to display a scheduled maintenance webpage on login.eplancare.com, informing users that the service was temporarily unavailable due to ongoing maintenance.
| Time | Action | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 04:30 | Sanity Check | Verified web UI, Tomcat access logs, and traffic monitoring |
| 04:40 | Drain ANS LB | Set all 4 Tomcat servers to drain mode (weight = 0) to stop new incoming traffic. Custom 503 maintenance page displayed to users accessing login.eplancare.com |
| 04:50 | Remove DNS A Record | Removed existing DNS A record pointing to ANS LB VIP (via Cloudflare Portal) |
| 04:55 | Sanity Check | Verification checkpoint |
| 05:00 | Switch to Cloudflare | Updated login.eplancare.com to point to Cloudflare LB |
| 05:05 | Sanity Check | Verification checkpoint |
| 05:15 | Extended Monitoring | Monitored traffic distribution through peak time (09:00) and throughout the day |
Rollback Plan
In the event of critical issues, I had a documented rollback procedure:
- Align with team - Confirm rollback decision.
- Remove CF LB DNS entry - Remove
login.eplancare.comfrom Cloudflare LB. - Disable CF pool - Disable server pool for Tomcat endpoints in Cloudflare.
- Restore ANS DNS - Revert A record to ANS LB Virtual IP.
- Enable ANS servers - Put all 4 Tomcat VMs back into load.
- Monitor and verify - Check traffic and review logs.
Note: Rollback was not required - included here for documentation completeness.
Results and Monitoring
Migration Outcome: Successful
Immediate Results
- Zero downtime experienced (beyond planned maintenance window)
- Seamless DNS cutover.
- First customer requests hit Cloudflare LB at 07:00 AM.
- Maintenance page successfully displayed during migration window.
Traffic Distribution
Load balancing was distributed across all 4 Tomcat instances (tomcat-01, tomcat-02, tomcat-03, tomcat-04) according to the configured weights:
- tomcat-01: Weight = 0.5 (~14% of traffic).
- tomcat-02: Weight = 1.0 (~28.5% of traffic).
- tomcat-03: Weight = 1.0 (~28.5% of traffic).
- tomcat-04: Weight = 1.0 (~28.5% of traffic).
This configuration was confirmed through Tomcat access logs and Cloudflare Analytics dashboard.
Traffic Patterns Throughout the Day:
The following screenshots from Cloudflare Analytics demonstrate consistent load distribution matching the configured weights at different times during migration day:
05:15 AM - Post-Cutover (Early Morning)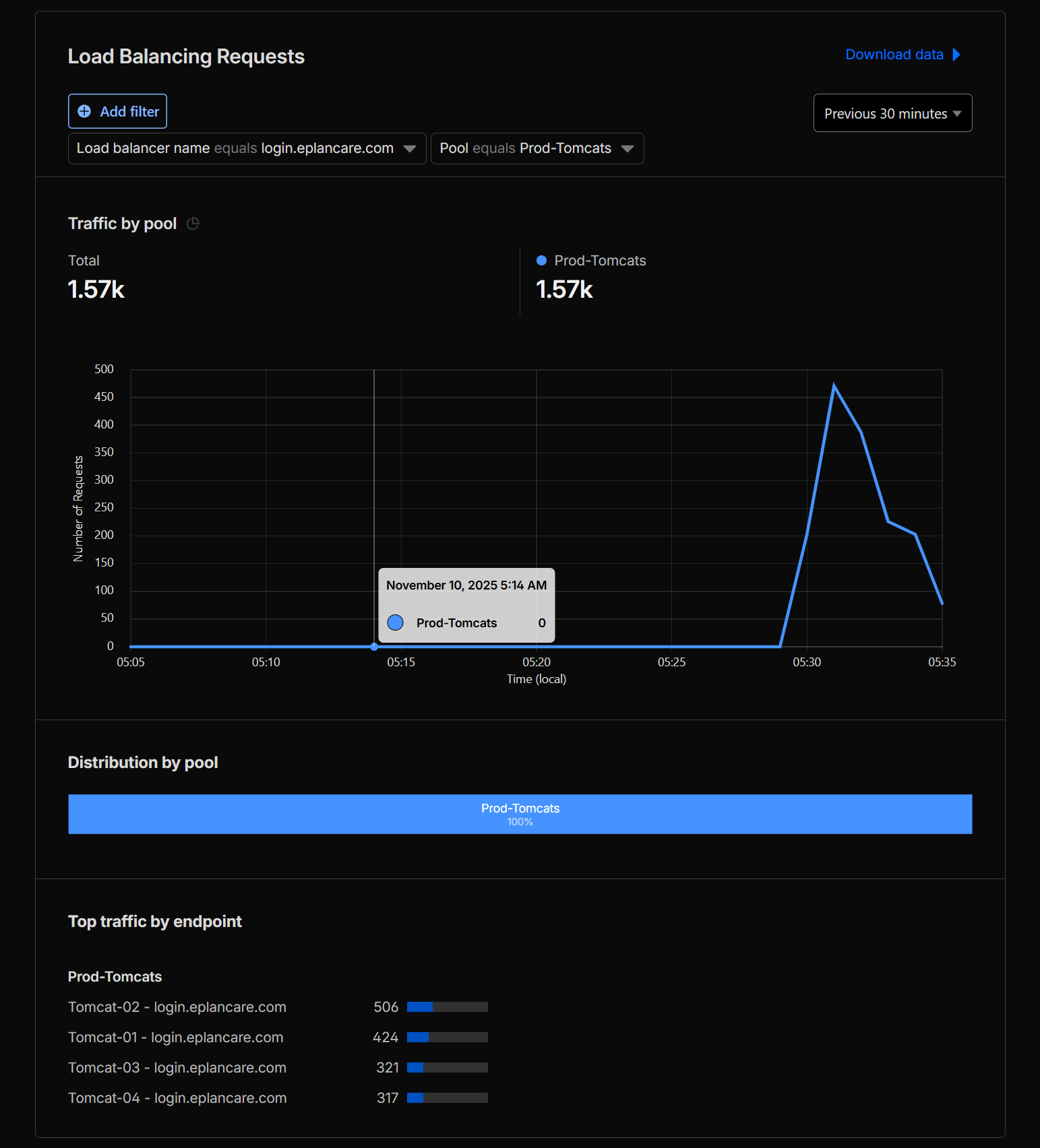
09:00 AM - Morning Peak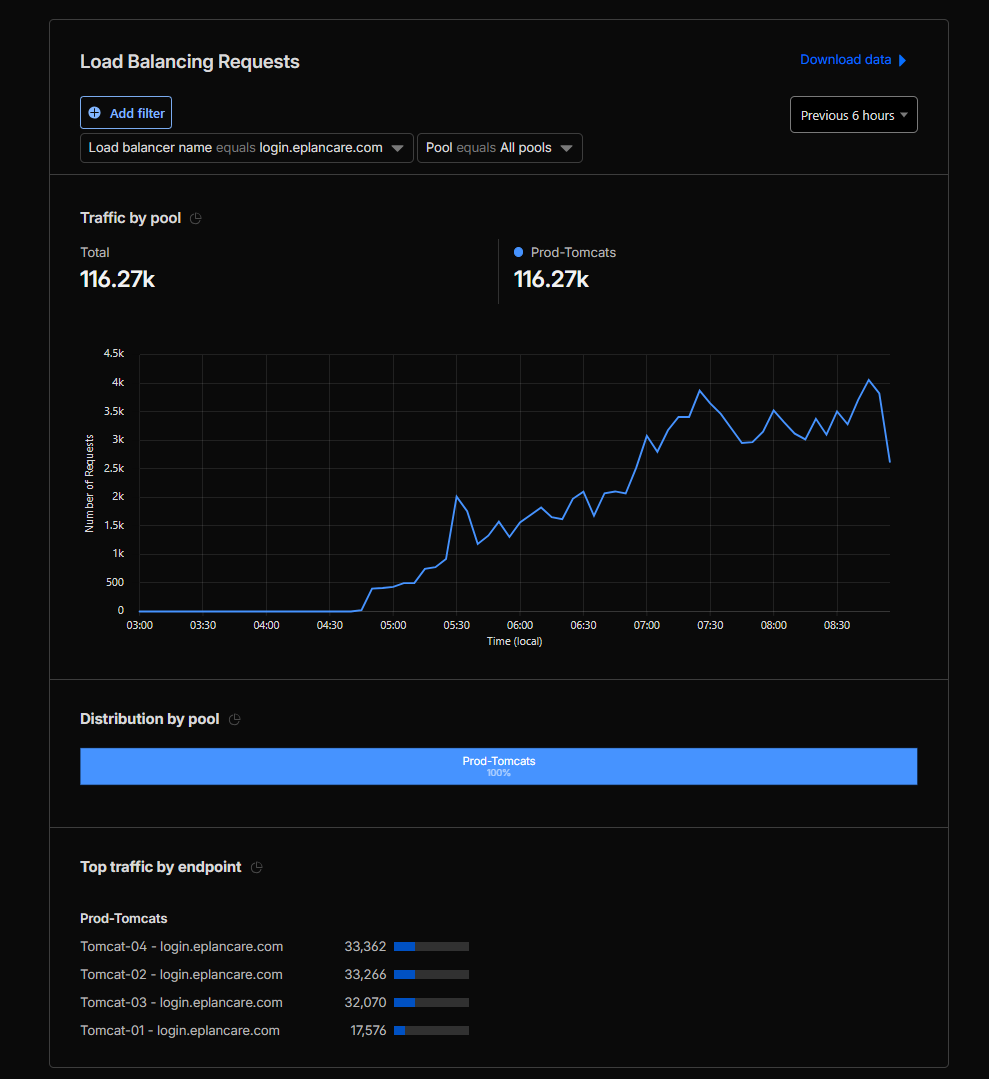
15:00 PM - Afternoon Activity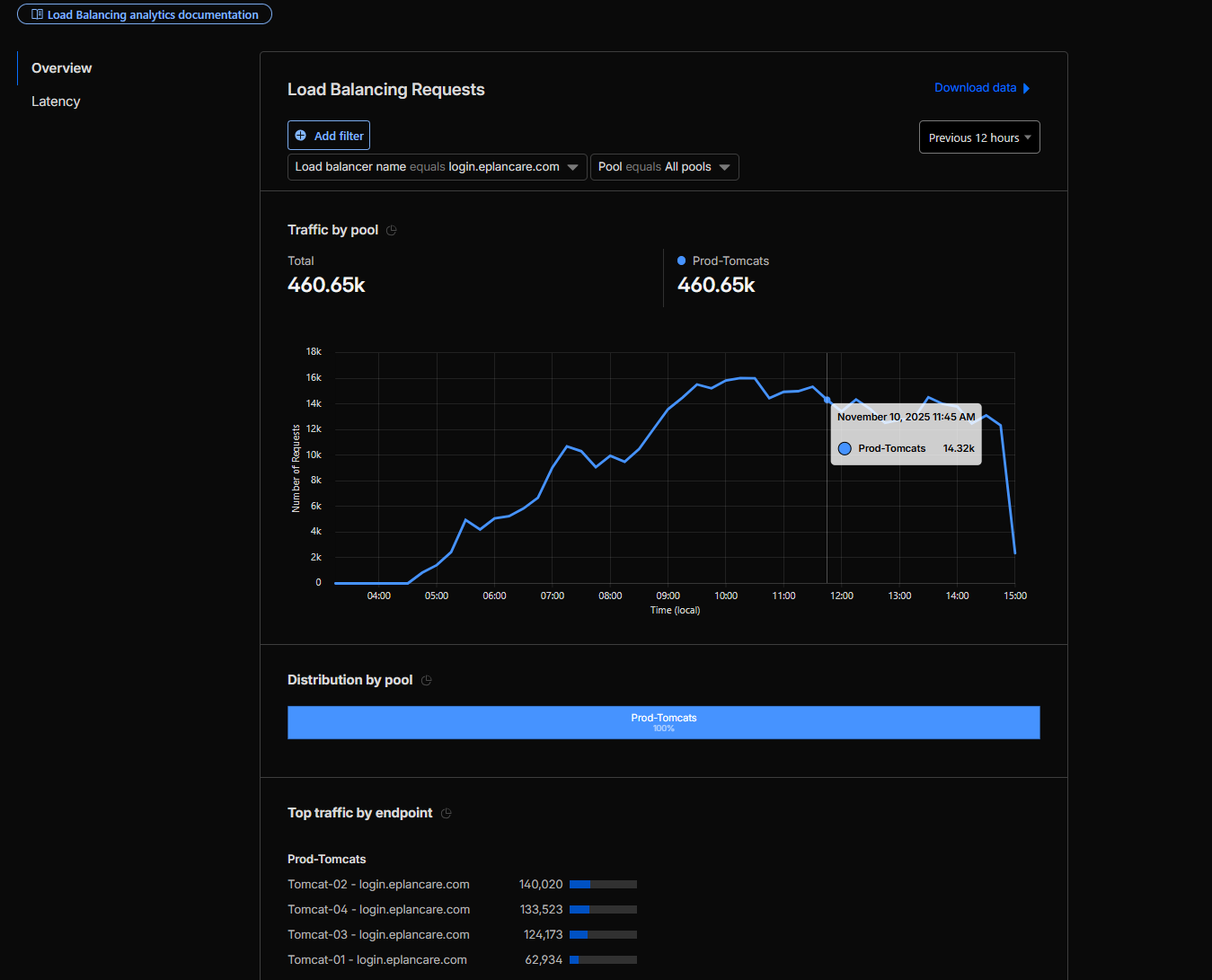
72 Hours Post-Migration - Sustained Performance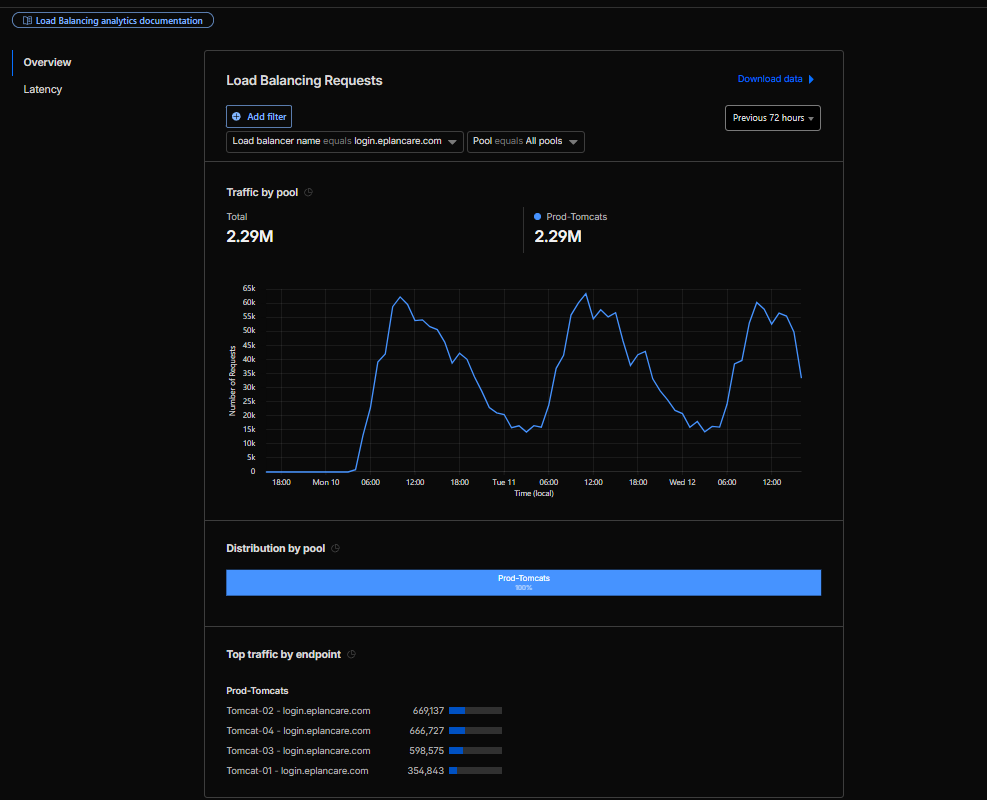
Traffic was monitored continuously through peak hours on migration day and for the entire week post-migration to ensure sustained performance and stability.
No Issues Observed
- No customer complaints.
- No application errors.
- No performance degradation.
Key Success Factors
What Made This Migration Successful
- Thorough Testing - Proof of concept in lower environment validated the approach.
- Meticulous Planning - Detailed implementation and rollback procedures.
- Pre-Configuration Strategy - Using dummy hostname allowed us to configure everything in advance.
- Timing - Executed during off-hours maintenance window
- Team Coordination - Proper change control and stakeholder communication.
- Extended Monitoring - Week-long monitoring ensured sustained success.
- User Communication - Custom 503 maintenance page kept users informed during migration.
Lessons Learned
Best Practices for Load Balancer Migration
Before Migration:
- Always conduct proof of concept in a non-production environment.
- Pre-configure as much as possible to minimise the cutover window.
- Practice rollback procedures, not just implementation.
- Use dummy hostnames for staging configuration.
- Prepare custom maintenance pages to communicate with users.
- Share high-level migration plan and readiness status with relevant team members.
During Migration:
- Schedule during maintenance windows.
- Build in multiple sanity check points.
- Drain traffic on all backend web servers simultaneously before switching to Cloudflare LB.
- Document every step with timestamps.
- Provide high-level progress updates to relevant team members at key milestones.
Post Migration:
- Monitor Cloudflare load distribution across all 4 Tomcat web servers.
- Monitor system and network performance.
- Inform relevant team members of migration completion and maintain open communication channels for any issues.